Navigating the world of e-commerce often involves grappling with numerous acronyms like EAN, GTIN, SKU. This jargon can be daunting, especially for newcomers.
However, understanding these terms is crucial for effectively managing your inventory and ensuring seamless operations.
The European Article Numbering (EAN) code, a cornerstone of the global retail system, is recognized in over 100 countries. These codes, comprising 12 or 13 digits and paired with barcodes, enable swift and accurate scanning at checkout points.
They streamline inventory management and facilitate international trade by adhering to global standards.
Moreover, as e-commerce continues to grow, significant marketplaces like Amazon and Google mandate using EAN codes for product listings, making them indispensable for online retailers aiming to reach a broader audience.
According to GS1, the organization responsible for EAN standards, over 6 billion barcodes are scanned worldwide daily, underscoring their importance in the retail ecosystem.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid grasp of what an EAN code is and why it’s essential for your store.
What is an EAN Code?

An EAN code, or European Article Numbering code, is a unique identifier for products predominantly used in European markets.
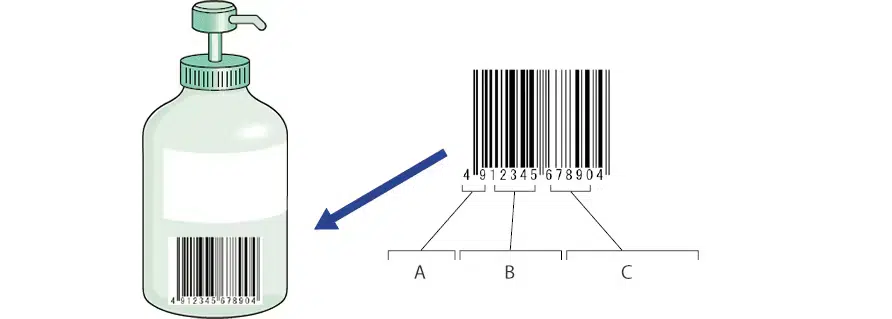
These codes consist of 12 to 13 numerical digits and are accompanied by a barcode. This combination allows for efficient and accurate electronic scanning and processing.
The EAN code serves as a product’s fingerprint—each code is distinct, ensuring no two items share the same identifier, which is vital for global commerce.
EAN codes significantly enhance inventory management by standardizing product identification. This standardization simplifies tracking items from the manufacturer to the retailer and eventually to the consumer.
For instance, a shampoo bottle sold in multiple countries will have the same EAN code, ensuring uniformity across different markets.
Businesses can use EAN codes to reduce human errors associated with manual data entry and product handling. This leads to more efficient operations, as products can be quickly scanned and tracked throughout the supply chain.
For example, a clothing retailer can swiftly check inventory levels, reorder stock, and manage sales data accurately.
The result is improved data accuracy, crucial for making informed business decisions.
Additionally, EAN codes facilitate better communication between suppliers and retailers. When a supplier ships a batch of products, the EAN codes ensure that both parties refer to the same items, minimizing the risk of confusion and errors.
For instance, a supplier of electronics can ship products to various retailers with confidence that the EAN codes will be recognized and processed correctly.
Why Should You Use EAN Codes?
Implementing EAN codes in your business can significantly enhance operational efficiency and market reach. Here are several compelling reasons to incorporate EAN codes:
1. Enhanced Product Identification
EAN codes provide a unique identifier for each product, making tracking and managing inventory easy. This precise identification reduces the chances of misplacing items and ensures that products are correctly logged in inventory systems.
2. Increased Market Reach
Major online marketplaces like Amazon and Google Shopping mandate the use of EAN codes for product listings. This requirement is particularly critical for sellers targeting European markets, as it opens up access to a broader audience and improves product visibility on these platforms.
3. Reduced Human Error
Standardizing product information with EAN codes minimizes the risk of errors associated with manual data entry. By using scannable barcodes, businesses can significantly reduce discrepancies in inventory records, leading to more reliable data and smoother operations.
4. Improved Customer Experience
Accurate product tracking ensures that stock levels are up-to-date, preventing situations where items are mistakenly shown as available or out of stock. This reliability builds customer trust and satisfaction, as shoppers are likelier to find what they need and receive their orders without issues.
5. Compliance with Global Standards
EAN codes adhere to international standards set by organizations like GS1, facilitating seamless global trade. This compliance ensures that products are consistently recognized and processed across different countries and regions, making international expansion and cross-border sales more straightforward.
Incorporating EAN codes into your business processes not only enhances efficiency and accuracy but also positions your products favorably in the competitive global marketplace.
Where Are EAN Codes Used?
EAN codes are essential in various retail and e-commerce sectors, ensuring efficient product identification and tracking. Here are some typical applications:
- Retail Stores: EAN codes are crucial at retail points of sale, allowing for quick and accurate scanning during checkout. For example, supermarkets use EAN codes to expedite checkout and manage inventory in real-time, ensuring products are readily available on shelves.
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon and eBay require EAN codes for product listings. This standardization helps customers find specific items easily and ensures sellers’ products are visible and searchable within these vast marketplaces. For instance, a smartphone listed on Amazon with an EAN code can be easily identified among similar products.
- Inventory Management: Businesses use EAN codes to track stock levels and product movement within warehouses. For example, a clothing retailer can monitor the inventory of various sizes and colors of a specific item, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
- Supply Chain Management: EAN codes facilitate smooth operations from manufacturers to retailers by providing a consistent product identifier. For instance, an electronics manufacturer can ship products to multiple retailers, confident that the EAN codes will ensure the products are correctly identified and processed at each stage of the supply chain.
Implementing EAN codes across these areas not only streamlines processes but also enhances accuracy and efficiency, making them indispensable for modern business operations.
Do All Products Need an EAN Code?
Not every product requires an EAN code. Here are some notable exceptions:
- Non-European Sales: Products sold outside Europe may not need an EAN code. Different regions often use other identification systems, such as North America’s Universal Product Code (UPC). For example, a retailer selling primarily in the United States typically uses UPC codes instead of EAN codes.
- Digital Products: Items that are not physical, such as software downloads, e-books, or online services, do not require EAN codes. These products are delivered electronically and are tracked using different methods that do not involve physical barcodes.
- Handmade and Custom Products: Unique, handcrafted items like artisanal jewelry or custom artwork usually do not need EAN codes. Platforms like Amazon allow sellers of such products to apply for exemptions. For example, an artist selling handmade pottery on Amazon can apply for an EAN exemption or use Amazon’s brand registry to list their products without needing standard barcodes.
Understanding these exceptions helps businesses determine when to use EAN codes and when alternative identification methods might be more appropriate.
How to Get EAN Codes – Step by Step
Obtaining EAN codes for your products involves a straightforward process through GS1, the global standards organization responsible for managing these codes. Here’s a detailed guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Register with GS1

Begin by visiting the GS1 website and creating an account. GS1 is the official source for EAN codes, ensuring they are unique and globally recognized. For example, if you are based in the United States, you would go to the GS1 US website.
Step 2: Choose a Subscription Plan
GS1 offers various subscription plans depending on the number of EAN codes you need. Small businesses might start with a plan with fewer codes, while larger companies may require a more extensive package. For instance, GS1 US provides different pricing tiers based on the number of GTINs (Global Trade Item Numbers) you need.
Step 3: Receive Your Codes
After selecting a subscription plan and completing the registration process, GS1 will issue your EAN codes. These codes are a series of unique numbers that you can use to label your products. The codes are usually delivered electronically and ready for integration into your inventory system.
Step 4: Implement the Codes
Apply the EAN codes to your product packaging. This step involves printing the codes on labels or the packaging itself. Incorporate these codes into your inventory management system to track products efficiently. For example, if you’re selling organic skincare products, each item will have a unique EAN code you can scan and monitor throughout the supply chain.
The GS1 UK website provides additional resources and a step-by-step guide on obtaining and implementing EAN codes. It also includes support and FAQs to assist you throughout the process.
For businesses looking to streamline their pricing and inventory management further, consider using Pricefy, a powerful tool designed to enhance e-commerce operations through competitor price monitoring and dynamic repricing.
Wrapping up
EAN codes are essential for modern e-commerce businesses, especially those operating in Europe.
They provide a standardized, efficient way to manage products, reduce errors, and enhance customer satisfaction.
By adopting EAN codes, you can streamline your operations and ensure your products are easily identifiable and compliant with global standards.