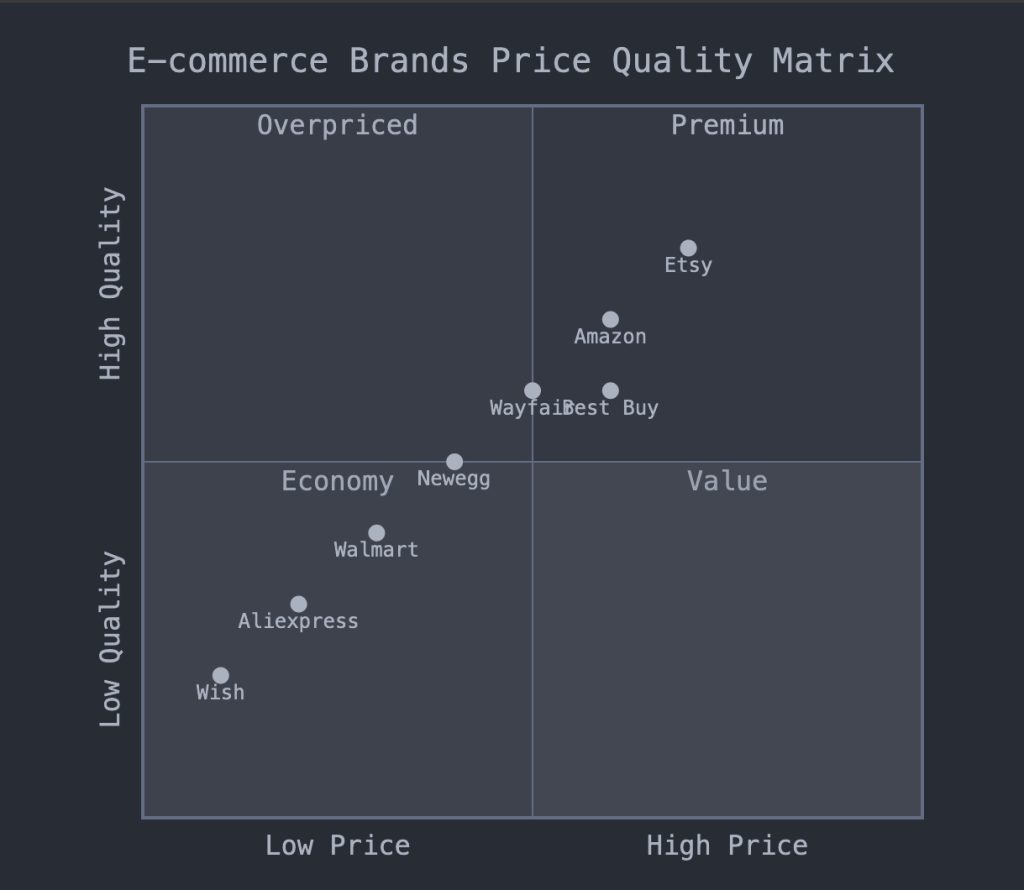
A Price Quality Matrix is a strategic tool used by businesses to analyze and visualize the relationship between price and quality across different products or services in a market.
This two-dimensional graph plots price on one axis and quality on the other, allowing companies to map their offerings against competitors and identify potential market opportunities.
By dividing the matrix into quadrants, businesses can categorize products as economy (low price, low quality), premium (high price, high quality), value (low price, high quality), or overpriced (high price, low quality).
This visual representation helps managers make informed decisions about pricing strategies, product positioning, and market segmentation, ultimately aiming to optimize their competitive advantage and profitability.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Price Quality Matrix
- How to Use the Price Quality Matrix
- The Benefits of Using the Price Quality Matrix
- Price Quality Matrix Examples
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Future Trends in the Price Quality Matrix
- Quick Tips for Using the Price Quality Matrix
- My Experience with the Price Quality Matrix
- FAQs
- Useful Links
- Conclusion
Understanding the Price Quality Matrix
At its core, the Price Quality Matrix categorizes products based on two key dimensions: price and quality.
By plotting these on a matrix, you can see where each product falls—whether it’s a premium offering with a high price and high quality, or a budget-friendly option with a lower price and quality.
This matrix is crucial for understanding how your product compares with competitors and where opportunities for repositioning might lie.
How to Use the Price Quality Matrix

1. Identify Key Products: Begin by selecting the products you want to analyze. These should be representative of your range, including best-sellers and underperformers.
2. Assess Quality and Price: For each product, determine its quality level and price point. Quality can be assessed based on customer reviews, material standards, and brand reputation.
3. Plot on the Matrix: Place each product on the matrix according to its price and quality. The matrix typically divides into four quadrants: economy (low price, low quality), bargain (low price, high quality), luxury (high price, high quality), and overpriced (high price, low quality).
4. Analyze Positions: Evaluate where your products are clustered. Are you positioned as a luxury brand, or do your products fall into the economy category? This analysis helps identify whether your pricing strategy aligns with your brand identity.
5. Adjust and Optimize: If your products are clustered in the “overpriced” quadrant, it might be time to either improve quality or reduce prices. Conversely, if they’re in the “bargain” quadrant, you could explore increasing prices or enhancing perceived value.
The Benefits of Using the Price Quality Matrix
Utilizing the Price Quality Matrix offers several compelling benefits:
- Competitive Positioning: Understand where you stand relative to competitors and identify opportunities to outmaneuver them.
- Customer Insight: Gain insights into what your customers value most—price or quality—and adjust your offerings accordingly.
- Strategic Pricing: Make informed pricing decisions that align with your brand and market position, increasing profitability and customer loyalty.
- Resource Allocation: Focus your resources on products that are strategically positioned to offer the best returns.
Here is a nice video from YouTube about Price Quality Matrix
Price Quality Matrix Examples
Let’s explore some real-world examples to illustrate how the Price Quality Matrix works:
Amazon
Amazon occupies a unique position in the Price Quality Matrix, straddling multiple quadrants but primarily situated in the value quadrant.
As one of the world’s largest e-commerce platforms, Amazon offers an vast array of products across all price and quality ranges. However, its private label brands, particularly AmazonBasics, exemplify its value proposition.
These products typically offer good quality at competitive prices, often undercutting brand-name alternatives. Amazon achieves this through economies of scale, efficient supply chain management, and data-driven insights into consumer preferences.
The company’s strategy of prioritizing customer satisfaction often leads to a balance of reasonable quality and competitive pricing.
Additionally, Amazon’s Prime membership program adds value through fast shipping and additional services, further solidifying its position in the value quadrant for many consumers.
Etsy
Etsy firmly positions itself in the premium quadrant of the Price Quality Matrix. As a marketplace for unique, often handmade or vintage items, Etsy caters to consumers seeking high-quality, distinctive products who are willing to pay premium prices.
The platform’s sellers typically offer artisanal, customized, or one-of-a-kind items that justify higher price points.
Etsy’s quality assurance comes from its community of skilled craftspeople and artists, many of whom use high-quality materials and time-intensive processes.
The platform’s focus on uniqueness and craftsmanship allows it to maintain higher prices while delivering products that meet or exceed customer expectations in terms of quality and originality.
This strategy has enabled Etsy to carve out a niche in the e-commerce landscape, appealing to consumers who prioritize individuality and are less price-sensitive.
Walmart
Walmart’s e-commerce presence positions the brand between the economy and value quadrants of the Price Quality Matrix. Known for its “Everyday Low Prices” slogan, Walmart consistently aims to offer products at highly competitive prices.
The quality of items ranges from basic to moderate, catering to budget-conscious consumers who prioritize affordability. Walmart achieves this positioning through massive scale, efficient supply chain management, and strong negotiating power with suppliers.
In the online space, Walmart has been expanding its marketplace to include third-party sellers, broadening its product range and occasionally pushing into higher quality territories.
However, the core of Walmart’s strategy remains providing accessible prices for a wide range of consumers, making it a go-to option for those seeking affordable everyday items without necessarily expecting premium quality.
Wish
Wish firmly occupies the economy quadrant of the Price Quality Matrix, known for offering extremely low-priced items often at the expense of quality.
The platform primarily caters to highly price-sensitive consumers who are willing to accept lower quality or longer shipping times in exchange for rock-bottom prices. Wish achieves this positioning by sourcing products directly from manufacturers, often in countries with lower production costs, and by keeping operational costs low.
The quality of items on Wish can be highly variable, with many products being imitations or simplified versions of brand-name goods.
This strategy has allowed Wish to capture a segment of the market that prioritizes price above all else, but it also comes with challenges such as customer satisfaction issues and a reputation for hit-or-miss product quality.
Newegg
Newegg positions itself primarily in the value quadrant of the Price Quality Matrix, especially in the electronics and computer hardware sectors.
The company offers a wide range of tech products, from budget-friendly options to high-end components, generally at competitive prices.
Newegg has built a reputation for providing good quality products, particularly appealing to tech-savvy consumers who understand product specifications and are looking for good deals.
The platform achieves this positioning by working directly with manufacturers, offering frequent sales and promotions, and maintaining a lean operational model.
Newegg’s focus on the tech niche allows it to cater to a specific audience that values both quality and competitive pricing in computer components and electronics.
Best Buy
Best Buy occupies a position slightly higher in both price and quality compared to Walmart, placing it between the value and premium quadrants of the Price Quality Matrix.
As a specialized electronics retailer, Best Buy offers a wide range of products from budget-friendly options to high-end, premium devices.
The company differentiates itself through strong customer service, including in-store experts (Geek Squad), which adds value and justifies slightly higher prices for some items.
Best Buy’s strategy involves price-matching policies to remain competitive while also offering exclusive deals and a curated selection of quality electronics.
This approach allows Best Buy to cater to a broad spectrum of consumers, from those seeking affordable electronics to tech enthusiasts looking for premium products with expert support.
Aliexpress
Similar to Wish, Aliexpress primarily occupies the economy quadrant of the Price Quality Matrix. As a platform that connects mostly Chinese sellers with global buyers, Aliexpress is known for its extremely low prices across a wide range of products.
The quality of items can vary significantly, from very low to occasionally surprising value for money. Aliexpress achieves its low-price positioning by providing direct access to manufacturers and wholesalers, cutting out middlemen, and leveraging China’s vast manufacturing capabilities.
While the platform does offer some higher-quality items, its primary appeal is to price-sensitive consumers who are willing to accept longer shipping times and potential quality inconsistencies in exchange for very low prices.
Aliexpress’s model has made it popular for consumers looking for affordable goods, especially in categories like electronics accessories, fashion items, and home decor.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
1. Overemphasizing Price: Focusing too much on price without considering quality can lead to misalignment with your target audience.
2. Ignoring Customer Perceptions: The matrix should reflect not only objective quality but also how customers perceive your products.
3. Stagnation: The market evolves, and so should your positioning. Regularly reassess your matrix to stay competitive.
Future Trends in the Price Quality Matrix
Looking ahead, the Price Quality Matrix is likely to evolve with new trends in e-commerce:
- Personalization: As AI and data analytics advance, businesses will be able to create dynamic, personalized price-quality matrices tailored to individual customers.
- Sustainability: Increasingly, quality will be defined not just by durability or design, but by ethical considerations, such as sustainability and sourcing.
- Real-Time Data: Real-time data integration will enable more responsive and adaptive pricing strategies.
Quick Tips for Using the Price Quality Matrix
- Regular Reviews: Periodically revisit your matrix to ensure your products are still well-positioned.
- Customer Feedback: Use customer feedback to adjust your quality assessments.
- Competitor Analysis: Keep an eye on competitors to ensure you’re not pricing yourself out of the market.
FAQs
Q: What is the pricing matrix tool?
A: It’s a tool that helps businesses determine the optimal price for their products based on various factors, including quality and competitor pricing.
Q: How do you create a Price Quality Matrix?
A: Start by listing your products, assessing their quality and price, then plot them on the matrix.
Q: What is quality-based pricing?
A: This strategy involves setting prices primarily based on the perceived quality of the product.
My Experience WIth Price Quality Matrix

As an e-commerce manager who has overseen multiple online stores across various niches, I’ve found the Price Quality Matrix to be an invaluable tool in shaping our pricing and positioning strategies. Over the years, I’ve managed everything from a budget-friendly electronics store to a premium artisanal food marketplace, and each presented unique challenges in balancing price and quality perceptions.
In my experience, the most successful approach has been to clearly define our position within the matrix and consistently align our product offerings, marketing messages, and customer service with that position.
For instance, when I managed a fast-fashion e-commerce site, we firmly positioned ourselves in the economy quadrant. We focused on trendy, affordable items and made it clear to customers that while our products weren’t designed for longevity, they offered great value for those wanting to stay current with fashion trends without breaking the bank.
Conversely, when I oversaw a high-end home decor store, we planted our flag squarely in the premium quadrant. Here, the challenge was justifying our higher prices through exceptional quality, unique designs, and outstanding customer service. We invested heavily in product photography, detailed descriptions, and a hassle-free return policy to build trust with our quality-conscious customers.
One of the most interesting experiences I had was with a consumer electronics store where we straddled the line between the value and premium quadrants. We offered a mix of affordable, high-quality own-brand products alongside premium branded items. This strategy allowed us to cater to both budget-conscious consumers and those seeking top-tier products. However, it required careful marketing to ensure we didn’t confuse our brand identity.
The Price Quality Matrix also proved crucial when we faced new competitors or market shifts. For example, when a new player entered the market with a similar positioning to our artisanal food marketplace, we used the matrix to identify opportunities to differentiate ourselves further. We ended up focusing more on the story behind our products and the exclusivity of our offerings, which helped us maintain our premium position and customer base.
One key lesson I’ve learned is the importance of constantly re-evaluating our position. Consumer perceptions of price and quality are not static, and what was once considered premium might become standard over time. This was particularly evident in the electronics store, where rapid technological advancements meant we had to continually adjust our product mix and pricing to maintain our desired position in the matrix.
Overall, my experience has shown that the Price Quality Matrix is not just a theoretical tool, but a practical framework that can guide decision-making across all aspects of e-commerce operations. From product sourcing and pricing to marketing and customer service, understanding and leveraging our position in the matrix has been key to the success of the various e-commerce ventures I’ve managed.
Useful Links
- Understanding the Price Quality Matrix: A detailed guide on what the matrix is and how to use it.
- Price Quality Matrix Template: Download a free template to start plotting your products today.
- Price Quality Matrix PDF: A comprehensive PDF guide to keep as a reference.
Conclusion
The Price Quality Matrix is more than just a tool—it’s a strategic asset that can transform how you price and position your products.
By understanding where your products stand and making informed adjustments, you can drive sales, increase customer satisfaction, and outmaneuver your competition.
Ready to make your pricing strategy unstoppable? Start by plotting your own Price Quality Matrix today.




